LoRaWAN Gateways – What You Need to Know!
LR & LoRaWAN are working alongside the 5th generation of radio frequency (RF) IoT technologies to transform wireless transmission and the Internet of Things! LoRaWAN is a network protocol built on LR, but many components within it enable it to work – like LoRaWAN Gateways! While gateways appear to be a relatively simple component in the LoRaWAN network architecture, there are still some key things that you should know. Join me in today’s article to learn more!
In this article, learn about the following and more!
- What is LoRa & LoRaWAN?
- What are LoRaWAN Gateways?
- What Characteristics of LoRaWAN Gateways Do You Need to know?
- Platforms for Building Your Complete LoRaWAN Network
- Seeed’s SenseCAP Ecosystem for Industrial IoT
- Hardware for Building Your LoRaWAN Network

What is LoRa & LoRaWAN?
To summarise simply, you can understand LoRa to be a type of hardware that supports long-range wireless communication, whereas LoRaWAN refers to a network protocol based on LR. I’ve already talked about the basics and benefits of LoRa & LoRaWAN in my Gentle Introduction to LoRaWAN Gateways & Nodes, so be sure to check it out first if you’re new to these topics!
Instead, this article will focus specifically on how to better make use of LoRaWAN Gateways when designing our LoRaWAN solution!
Now then, what are LoRaWAN Gateways?
LoRaWAN Gateways are one of four key components of the LoRaWAN network architecture:
- End Nodes – Represents edge devices or sensors
- Gateway – Collects or concentrates data from several end nodes
- Network Server – Consolidates data from gateways for upload to application server
- Application Server – Processes or displays consolidated data
By definition, a gateway refers to a device that acts as a gate between two networks to allow network traffic to flow in and out of the network! For example, routers, firewalls or servers are considered network gateways in their own right.
Quite similarly, LoRaWAN Gateways in a LoRaWAN network are bridges between End Nodes and the Network Server. To receive information from the End Nodes, gateways are equipped with a LoRa concentrator and can, in essence, be considered as a router of sorts. Two primary types of LoRaWAN Gateways are differentiated by their type of software:
- Minimal firmware that only runs the packet forwarding software to the network server.
- Operating system where the packet forwarding software is run in the background. While this consumes more power, gateway administrators are able to utilise the gateway device for other purposes.
It is important to distinguish that LoRaWAN End Nodes communicate with LoRaWAN Gateways through low-power LoRaWAN, whereas Gateways communicate with the Network Server through higher bandwidth communication protocols like WiFi, Ethernet, or Cellular!
What Characteristics of LoRaWAN Gateways Do You Need to know?
The most basic function of LoRaWAN Gateways is to simply demodulate LR packets from end nodes and transfer them to the server, but there are still several key elements you have to be aware of when working with LoRaWAN Gateways or LoRaWAN networks in general.
Gateway Forwarding Protocols
The Packet Forwarder is the software that provides the core functionality of a LoRaWAN Gateway, and defines the method of that is used to receive LR packets and transmit them to the network server.
For example, the Semtech UDP Packet Forwarder is the original LoRaWAN packet forwarder, and uses the Semtech UDP protocol for transmission. Today, most gateways include a pre-compiled version of the Semtech UDP Packet Forwarder, often adapted to the specific gateway. Another popular packet forwarding protocol is MQTT which is used with the popular Chirpstack server infrastructure.
Frequency Plans
LoRaWAN operates in the unlicensed radio spectrum, which means that it is free to use without having to obtain transmission rights. Yup, this also means that anyone can buy equipment and set up their own LoRaWAN network without a license or permit.
However, LoRaWAN is not without its limitations – it is, in fact, quite the opposite. Because LoRaWAN operates with lower radio frequencies to achieve longer range, there are often restrictions that are country-specific. To combat this, LoRaWAN usage and equipment is designed for a number of frequency bands that are allowed for use in different regions.
Nonetheless, two common bands that you may come across are 915MHz for Australia & North America, and 868MHz for Europe. In some other regions, you may be granted the flexibility to use more than one frequency plan. For quick reference for the frequency plans available to your local use, you may wish to visit Frequency Plans by Country on The Things Network’s website.
Note: It is important to use the correct frequency band for your region, as failure to comply can be punishable by law!
Duty Cycles
A duty cycle is defined as the fraction of time that transmission occurs. For example, if a device is transmitting on a given channel for two seconds in a 10 second time frame, it is said to have a duty cycle of 20%. It is important to consider that if a device transmits on a different channel but in the same timeframe, it will also be included in the calculation of the duty cycle.
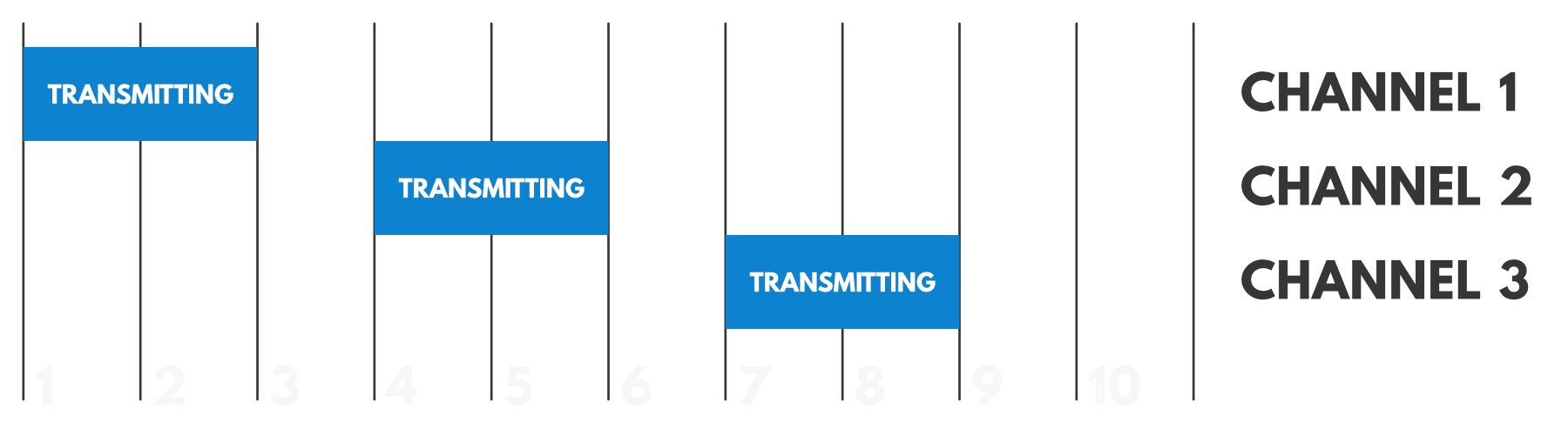
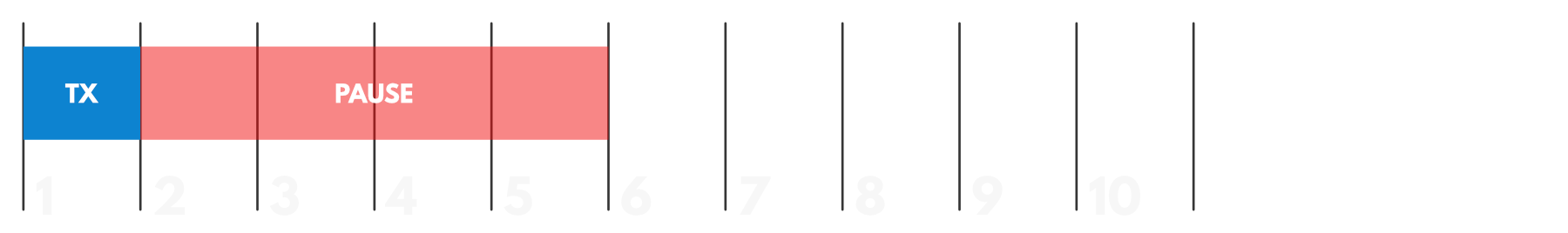
Why talk about duty cycles? Well, apart from transmission frequency, duty cycles are actually often regulated by governments as well. In most cases, this duty cycle is commonly set to 1% – so it’s important to be aware of how frequently you need your devices (both LoRaWAN Gateways and Nodes) to communicate! To comply with duty cycle regulations, a pause is programmed to follow each transmission.
Device Identification
To keep up with the scale of devices in a LoRaWAN network, there are certain addressing measures that are taken to configure and identify each device – LoRaWAN Gateways included!
- DevEUI – 64 bit end-device identifier, EUI-64 (unique)
- DevAddr – 32 bit device address (non-unique)
- AppEUI – 64 bit application identifier, EUI-64 (unique)
- GatewayEUI – 64 bit gateway identifier, EUI-64 (unique)
The GatewayEUI is a unique identifier that is manufactured together with the gateway itself, and is used to connect to LoRaWAN cloud platforms like The Things Network. According to TTN, there’s no need to worry if your gateway did not come with an embedded EUI, as you can also utilise an MQTT-based forwarder that only requires a Gateway ID, that can be chosen by yourself.
Regional Parameters
In addition to frequency plans and duty cycles, there may be other restrictions imposed on the use of LoRaWAN in your area. For example, certain hardware certifications may be required beyond basic compliance with regulations. In this case, the best course of action is to refer to the official LoRa Alliance® Website, which has the full documentation on standards, interfaces, parameters and certification programs!
Platforms for Building Your Complete LoRaWAN Network
While you can build a private LoRaWAN network with just a gateway and some end devices, or even simply use direct transmission without LoRaWAN like in LR P2P Communication, the benefits of long range, large scale networks truly shine when paired with an appropriate LoRaWAN server. In this section, we’ll cover the most popular platforms to help you build your complete LoRaWAN Network!
The Things Network (TTN)

The Things Network is a member of the LoRa Alliance® and provides a set of open tools and global network for building IoT applications. They also host a global collaborative network of LoRaWAN peers, which means that you can take advantage of existing LoRaWAN Gateways in their network to forward data to your application in the cloud! You’ll also be excited to know that their community edition is free for fair use, so you can use it as a starting ground to explore building your IoT applications!
SenseCAP Portal

The SenseCAP Portal is part of Seeed’s SenseCAP Ecosystem, which is a complete package to fuel your IoT applications with absolute compatibility with industrial grade sensors and LoRaWAN gateways. Built on Microsoft’s reliable and secure Azure IoT platform, the SenseCAP portal also allows you to use the SenseCAP API to easily manage your LoRaWAN devices and their communications through a variety of protocols, including HTTP, MQTT and Websocket!
Azure IoT

The IoT platform from Microsoft needs no introduction. Today, Azure IoT is one of the most popular cloud platforms for building large scale IoT applications including those with LoRaWAN. In 2019, Microsoft also implemented their Azure IoT Central Device Bridge in collaboration with TTN, which now makes it trivial to connect LoRaWAN applications through Azure’s services!
You can even use Azure to host your very own LoRaWAN network and server. Visit this blog post by Benjamin Cabé for more information!
Seeed’s SenseCAP Ecosystem for Industrial IoT
At Seeed, we are committed to developing industrial-grade IoT products and solutions to help you meet any kind of industrial IoT needs. Seeed supports industrial transformations through hardware in our SenseCAP Series: SenseCAP Sensors, SenseCAP LoRaWAN Gateway; and a complete suite of supporting software like the SenseCAP Portal, SenseCAP App, SenseCAP API and SenseCAP Dashboard.
By building a vast LoRaWAN network that is then connected to servers in the cloud, a diverse range of solutions can be developed for any business problem, regardless of the intended application in monitoring, control or maintenance!
Note: Before purchasing any of the following products, please ensure that you have selected the correct frequency band for your region! For more details, please once again visit this Frequency Plan by Country on The Things Network’s website.
Build Your LoRaWAN Network!
The many components of the network infrastructure can be confusing. However, picking the right hardware is often the simplest yet most important way to start! Here are some product recommendations to help you start building your very own LoRaWAN network!
SenseCAP LoRaWAN Outdoor Gateway
Seeed’s SenseCAP LoRaWAN Gateway collects, aggregates and uploads data from your sensors in the field to the cloud for easy access and further action. The SenseCAP LoRaWAN Gateway is equipped with a high-performance processor AM3358 and the telecom-operator-level LR chip, SX1301 to ensure robustness and high performance in large-scale networks. In addition, it includes mutual authentication and encryption for added security! With added compatibility with the SenseCAP Portal, it’s easier than ever to build your LoRaWAN solution!
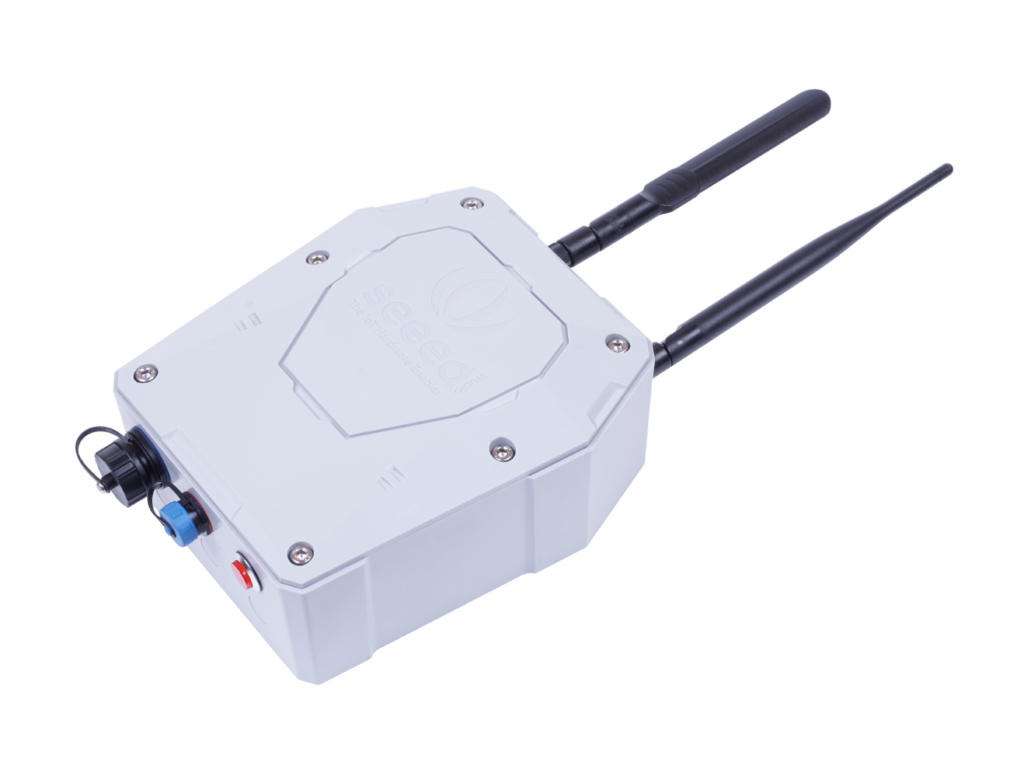

Product Features:
- High-performance Cortex A8 1GHz processor, Linux system.
- Supports LoRaWAN protocol Class A, support ultra-low-power SenseCAP Sensor
- 8 RX, 1 TX transceiver, maximum transmit power 27dBm
- Multiple ISM bands: CN470, EU868, US915
- Internet Access via 4G or Ethernet
- Ultra-long Distance Transmission: 10km with Line-of-Sight, 2km in Urban Environments
- Industrial grade protection: IP66 enclosure, temperature -40℃~70℃, suitable for outdoor applications
- Easy deployment and rapid provisioning
Visit the Seeed Online Store for more information on the SenseCAP LoRaWAN Gateway, as well as a quick tutorial on how to get started!
SenseCAP M2 Multi-Platform LoRaWAN Indoor Gateway(EU868, US915, AS923, AU915)
SenseCAP M2 Multi-Platform LoRaWAN Gateway is a standard LoRaWAN gateway that supports connecting to different network servers. It supports global LoRaWAN frequency plans from 865 MHz to 923 MHz and can be used in multiple LoRaWAN applications like smart buildings, environmental monitoring systems, precision farming, etc.
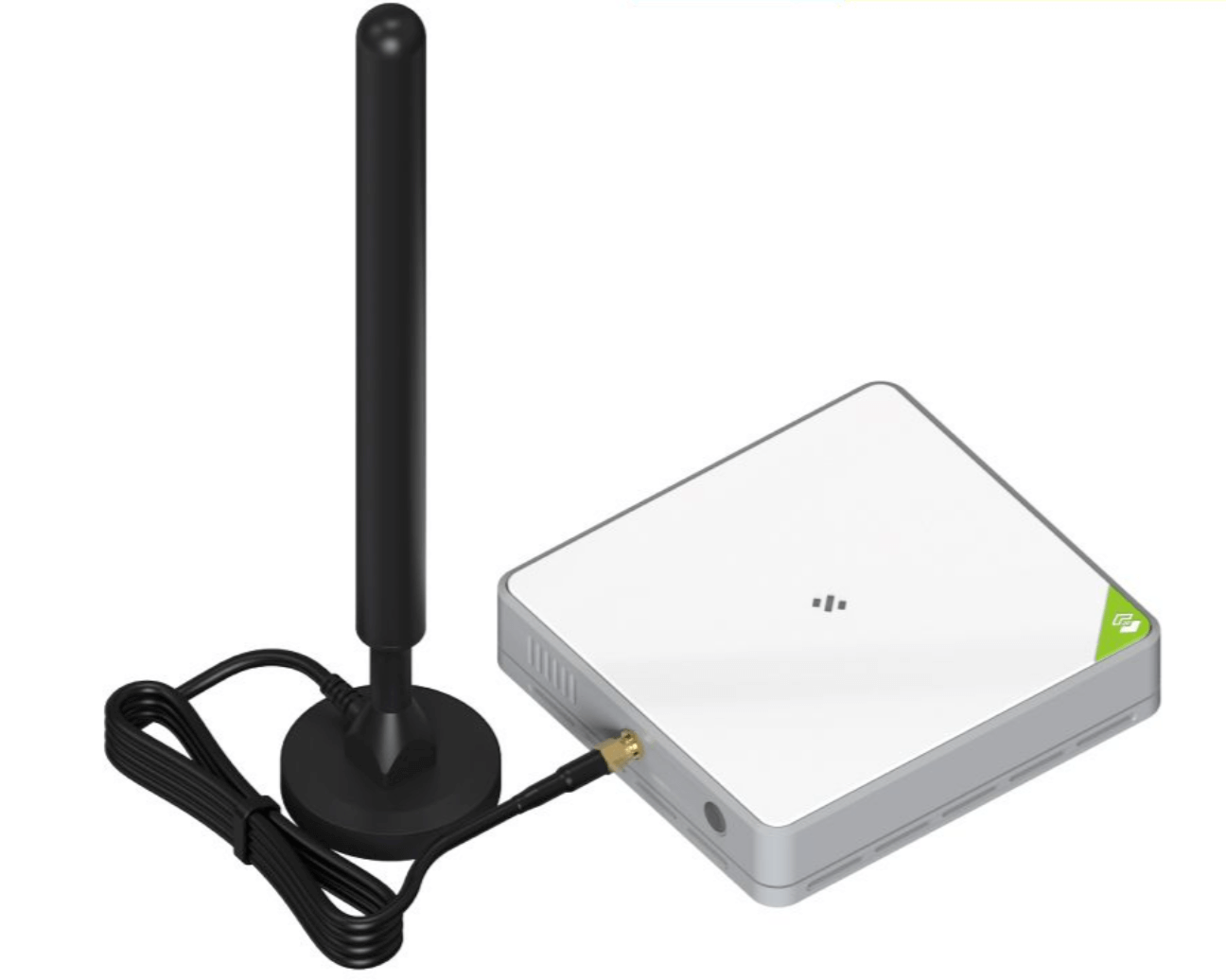

Product Features:
- Up to 10km of LoRaWAN® coverage and strong signal, allowing users to send data with extremely long ranges at low data rates.
- Compatible with multiple LNS like AWS, TTN, ChirpStack, etc. via using the Packet Forwarder / Basic Station mode.
- Based on Chirpstack, provides a fast and reliable solution for launching a LoRaWAN network.
- The PoE feature is also added to this device, making your deployment more reliable and faster.
- Supports Cellular(optional)、Wi-Fi and Ethernet for internet backhaul.
To learn more about the SenseCAP M2 Multi-Platform Indoor Gateway, click the product page on the Seeed Online Store.
Wio-E5 Development Kit
The Wio-E5 Development Kit consists of the Wio-E5 Development board, an antenna, a USB Type C Cable and a 2*AA 3V Battery Holder. The Wio-E5 Dev Board is embedded with the Wio-E5 STM32WLE5JC module with LoRaWAN protocol compatibility on the global frequency band. In addition, it supports various data protocols and interfaces, such as full GPIOs, RS-485 and Grove!
Product Features:
- Ultra-low power consumption and high performance
- Easy testing and rapid prototyping
- Full GPIOs that lead out to rich interfaces, including RS-485, Grove, and etc.
- Global LoRaWAN® and LR frequency plan supported
- Long-distance transmission range to 10km (ideal value in open area)
If you’re keen to pick up the Wio-E5 Development Kit, visit the Seeed Online Store now!
The Wio E5 Development Board is part of the Wio E5 Series, which is built around the Wio E5 STM32WLE5JC module that has been designed with an ARM Cortex-M4 core and the SX126x LR module. You can also choose from a mini Dev Board, Grove module, or order the Wio E5 module itself for your custom designs!
Summary & More Resources
LoRaWAN gateways are an extremely important component of the network architecture that enables the wide coverage that LoRaWAN is prized for. While their function appears to be simple, I hope that you’ve gotten a better insight on the considerations that you should make when choosing a gateway or designing your LoRaWAN solution!
To learn more, please visit the following resources!
- What is Peer-To-Peer (P2P) LoRa Communication?
- IoT in Smart Agriculture: LPWAN Technologies & Applications
- How to Enable LoRa and LoRaWAN on Arduino and Raspberry Pi
- How Machine Learning has Transformed Industrial IoT